Magnetic drive pumps, also called magnetic pumps, are a kind of non-contact torque transfer using magnetic coupling, belonging to a kind of centrifugal pumps, whose main feature is to drive the pump shaft through the non-contact coupling of internal and external magnets, this design removes the traditional sealing system and effectively avoids the problem of leakage, and the magnetic drive pumps are the ideal choices for dealing with high-risk or corrosive liquids.
In a magnetically driven pump, magnets are used to transmit power. The rotational torque is usually transmitted through a pair of magnets from the driving end (motor side) to the pump body end (driven side). The magnets on the motor side drive the magnets on the pump body side through an external magnetic field to rotate the pump's rotor, which drives the fluid delivery.
Common magnets in magnetic drive pumps are rare earth NdFeB magnets and rare earth SmCo magnets, of which, NdFeB is more magnetic than SmCo in the same size, and high grade NdFeB magnets (e.g., N42, N48, N52 grades, etc.) are usually used in magnetic drive pumps. However, the disadvantage of NdFeB magnets is that they are susceptible to moisture and corrosion, so they need to be treated with anti-corrosion treatment, such as adding black epoxy protective coating to the surface. For some demanding applications, especially in high temperature environments, Samarium Cobalt magnets are more suitable than NdFeB magnets. Although its magnetic properties are slightly inferior to NdFeB, it performs better in high temperature and strong corrosive environment.
Magnetic pump magnetic drive structure schematic picture
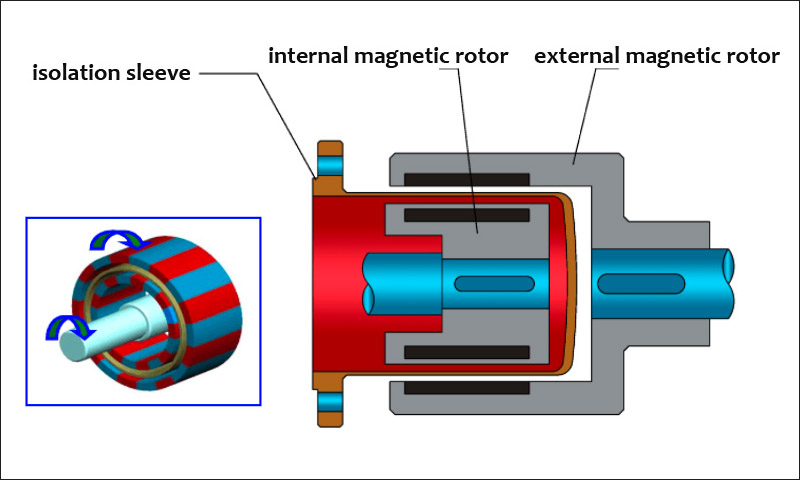
Due to the presence of the isolation sleeve, there is no direct contact between the inner and outer magnets, thus ensuring the sealing performance of the pump.
Magnetic drive pump magnet shape, pole arrangement and layout
The shape is mainly ring-shaped and fan-shaped, of which the ring is the most common, inside and outside the rotor are ring-shaped design, easy to install and uniform distribution of magnetic field. Sector magnets are also more common, by a number of pieces of sector magnets spliced into a ring, suitable for large size pumps, easy to manufacture and maintenance.
There are three main types of magnet layout, distribution of internal and external rotor layout, coaxial layout, multi-pole layout. Inside and outside the rotor layout of the outer rotor for the driving magnet, the inner rotor for the follower magnet, the two through the magnetic field coupling transfer power. Coaxial layout driving and driven magnet coaxial arrangement, compact structure, suitable for small pumps. Multi-pole layout magnets are arranged in multi-pole arrangement to enhance the magnetic field strength and uniformity, and improve the torque and efficiency.
For the magnetic pole arrangement, there are NS alternate ranking and Halbach array. The Halbach array is a special arrangement that enhances efficiency by strengthening the magnetic field on one side and weakening it on the other.
When selecting magnets for magnetic drive pumps, the magnetic properties of the material, operating temperature, corrosivity, size, cost and other factors should be considered. Neodymium-iron-boron magnets are suitable for most standard applications, and samarium-cobalt magnets are suitable for high-temperature environments (temperature resistance up to 350°C).
Related Product Recommendations;
 China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier
China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier 


