The best example of a magnet is the Earth. If we think of the Earth as a large magnet, then the Earth's geomagnetic north pole is the S pole and the geomagnetic south pole is the N pole. The north pole of the earth's geomagnetic field is the S pole, and the south pole of the earth's geomagnetic field is the N pole. The north pole of the earth's geomagnetic field is the S pole and the south pole of the earth's geomagnetic field is the N pole.
Since a magnet is called a magnet, it can attract an object that generates a magnetic field other than iron, in simple terms a magnet is a product of iron ore, and in a broader sense a magnet is an object or device used to generate a magnetic field that attracts ferromagnetic substances such as iron, nickel, and cobalt, among other metals.
The magnetic moment of a magnet is a vector that describes the overall magnetic properties of a magnet. While a magnet generates a magnetic field, it is also subject to an external magnetic field, and when placed in an external magnetic field generated by another coil or magnet, the magnet is subjected to a torque that attempts to square its magnetic moment to the magnetic field, and a magnet in an applied magnetic field may also be forced to move in a particular direction if the magnetic field does not vary with space. If the magnetic field does not vary in space, the net force on the magnet is zero.
N S pole of an arc magnets
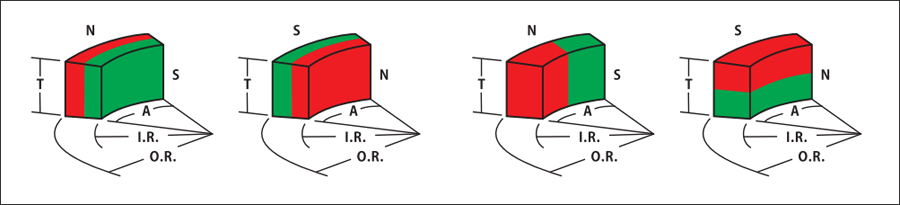
The structure of N and S poles of a magnet;
N Pole: The pole where the magnetic rod points to the north is called the “North Pointing Pole”, or “N Pole” for short.
S Pole: The pole where the rod points to the south is called the “Guide Pole”, abbreviated as "S Pole".
No matter how the magnet is cut, the N-pole and S-pole cannot be separated. When a magnet is broken, a new pole will be created at the break and become two new magnets. When a magnet is broken, a new pole will be created at the break and two new magnets will be formed. The two ends of the magnet, either N-pole or S-pole, are the areas with the strongest magnetism, called poles, and the center part has the weakest magnetism, called the “neutral zone”, and no new pole will be created when the magnet is cut along the NS line, while a new pole is created when it is cut perpendicularly to the NS line.
Magnets with multiple poles;
Related articles on magnet poles;
 China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier
China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier 


