Magnets, we are no strangers, most of the magnets we buy and see on a daily basis are permanent magnets, which have long-lasting magnetism and play an important role in our daily lives. Whether it is household appliances, office equipment, or high-tech products, there are magnets, and today we introduce its nemesis - heat.
Yes, heat weakens the magnet's magnetic ability.
Heat affects magnets in two ways: it reduces the magnet's remanence, and it reduces its coercivity. The remanent magnetism refers to the magnetization strength retained by the magnet in the absence of an applied magnetic field, while the coercivity represents the magnet's ability to resist changes in the direction of magnetization by an external magnetic field. These two parameters determine the actual magnetic properties of the magnet.
The following picture shows a comparison of the properties of permanent magnet materials (maximum magnetic energy product, Curie temperature, maximum operating temperature, price).
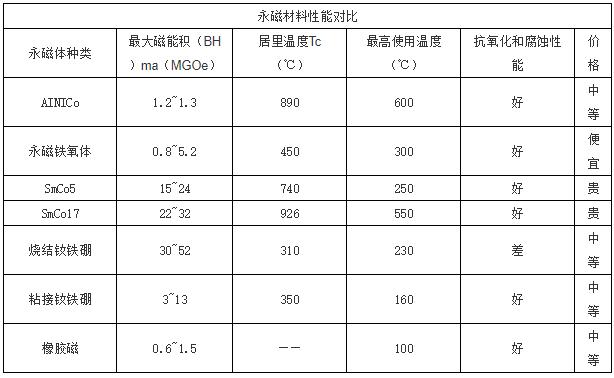
When the temperature rises, the thermal movement within the magnet intensifies, disrupting the arrangement of the magnetic moments and thus weakening the overall magnetizing strength. For most magnet materials, the remanent magnetization decreases by about 0.1% for every 1 degree Celsius of temperature increase. When the temperature reaches a certain level, called the Curie temperature of the ferromagnet, the magnet will lose its magnetic properties completely. The Curie temperature varies from material to material, but is usually in the hundreds of degrees Celsius.
In addition to remanent magnetization, heat also affects the coercivity of a magnet. The temperature coefficient of coercivity is generally in the range of -0.2% to -0.6% per degree Celsius. Excessive temperatures cause the magnet to lose its coercive torque and become more susceptible to changes in the direction of magnetization by an external magnetic field.
In practice, the performance of magnets can be significantly affected by changes in temperature. For example, magnets used in motors and generators need to be kept at a low operating temperature to ensure their magnetic stability. If the temperature of the operating environment is too high, the magnet's magnetic properties may weaken significantly, thus affecting the efficiency and performance of the device. Additionally, in hard disk drives where data is stored, the stability of the magnetic material is also closely tied to temperature, and excessive temperatures can lead to data loss or equipment failure.
Despite their special permanent magnetic properties, magnets are not truly permanent. Heat, as the magnet's nemesis, will bring certain effects and limitations to this amazing material. Only by fully recognizing and reasonably dealing with the effects of heat can the excellent performance of magnets be maximized.
Heat-resistant magnets are recommended;
You may also want to know;
Neodymium grade strength and temperature resistance chart
Temperature coefficient and characteristic curve of neodymium magnets
Temperature Characteristics and Coefficients of Ferrite Magnets
Do neodymium magnets demagnetise at transient high temperatures?
 China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier
China Neodymium And Ferrite Magnets Manufacturer & Supplier 


